LinuxCareer's IT Skills Watch tracks IT skills demand leaning towards the Linux and Unix environment and reports the IT skills that are required by employers seeking Linux talent. Furthermore, the skills are sorted by the frequency they appear in such job advertisements. This report aims to extend the study of the IT Skills Watch by identifying which skills are grouped together in IT job advertisements. By employing cluster analysis LinuxCareer.com identifies 10 relatively different groups of skills that can be linked to IT job categories. The winner set of IT skills is also identified, which suggests the most popular, in terms of demand, IT qualification.
IT Skill Sets Study Design
Similarly as the July IT Skills Watch, the number of analyzed Linux job ads is approximately 10,000. A job advertisement is classified as a “Linux job ad” when knowledge of Linux is required by employers to some extent from candidates for such position. This includes either extensive or only basic knowledge of this operating system. The analyzed job ads were posted around the world between May and June 2013. This gives us a recent, representative sample of data for the Linux job market. The job ads are then checked against approximately 150 IT skills, dozen operating systems and hundreds network protocols. Scores are then reported in the July IT Skills Watch. For this report, only skills that reach the score of over 300 are chosen for analysis. That is, we take into account all 40 IT skills, first 9 network protocols, 19 development skills, 3 top certificates and first 8 operating systems.
Clustering of IT skills
Without going too much into technical details of our analysis, it suffices to say, that LinuxCareer.com computes a coefficient of relation between two skills for the job advertisement data. Such coefficient tells us what skills are related and what is the strength of such relation. In general, all pairs of skills are checked for their common appearance in Linux job ads and if their frequently appear together the coefficient is appropriately higher.
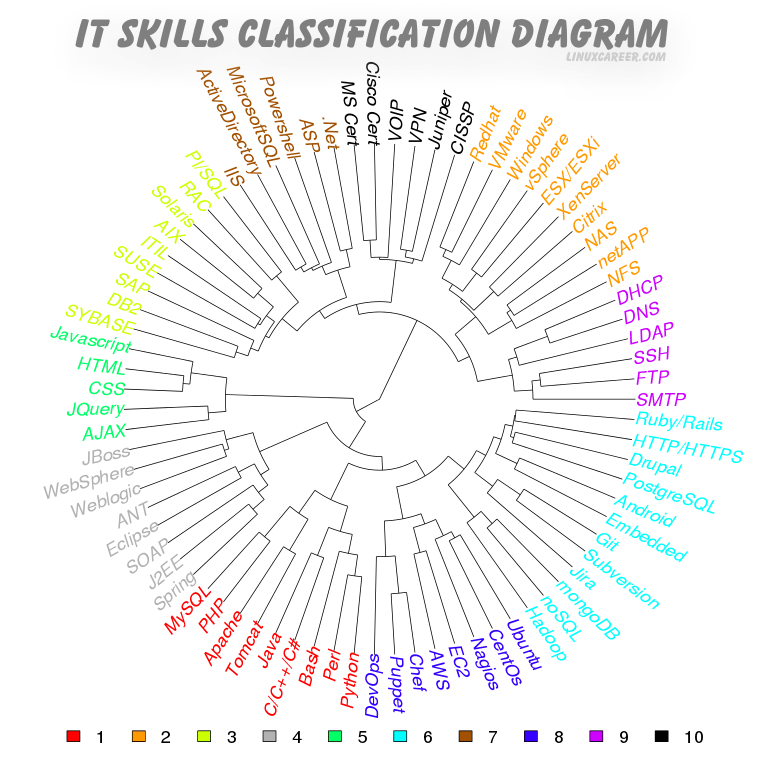
This lets us to cluster skills into groups that relate to Linux job categories.
The IT skills classification diagram[1] below illustrates 10 clusters/sets of skills that were identified by cluster analysis[2]. The legend below the graph shows the group reference number, which is linked to such sets of skills by color. The identified groups vary in size from 5 to 12 elements. It does not mean, however, that you need to be familiar with all the skills in a given group to apply for a relevant Linux job. On the contrary, it is rarely the case that the employer require you to have all the skills from the given group. Note that the identified ten groups can be further split into segments. It is also important to point out that the groups may cover more than one Linux job title.
IT skills classification diagram interpretation
The IT skills classification diagram was obtained by employing cluster analysis. Therefore, the closer given two skills are in the diagram, the more often they appear together in a job advertisement. Interestingly, the diagram seems to form two distinct groups. First group can be described as open source programming and web development tools, which covers clusters 5, 4, 1, 8 and 6. The second one is more relevant to networking and information systems and can be associated with proprietary software. This group comprises clusters 2, 3, 7, 10 and 9.
Group six, as the largest one, contains a range of qualifications. First level qualifications include Web and Applications Development. That includes Ruby and Rails Developers, Drupal Developers and Embedded Devices Developers. This segment is then linked with group of skills related to bug tracking, software versioning and source code management (Jira, Subversion, Git). Such skills, of course, are very useful to developers. On top of that, the third segment rounds up this cluster of skills with qualifications related to databases and large data management. As you can see, even though this large group of skills can be split to three segments, joining of such subgroups makes perfect sense.
There is a number of other interesting observations based on the LinuxCareer’s IT skills classification, which further proves the validity of our analysis. For instance, there is an evident connection of Redhat with VMware in the cluster number 2, which is explained on the vmware blog:
“Red Hat and VMware are collaborating to support joint customers who are transforming their data center network operations and economics through network virtualization. Red Hat will distribute and support the platform software Red Hat Enterprise Linux and Red Hat OpenStack, including Open vSwitch, and work together with VMware to support joint customers who chose to run VMware network virtualization software on the Red Hat platforms.”[3]
Moreover, group 3 reflects a forming SUSE and SAP alliance[4] and SUSE’s Unix to Linux migration effort[5]. Group 10 reveals that Cisco jobs are closer to MS Windows environment from which we can conclude that no extensive knowledge of Linux is required by employers. Group 8 suggests that Amazon Web Services (AWS) are closely tied to open source configuration management tools such as Puppet and Chef. Additionally, it seems that most AWS server deployments tend to be implemented on such operating systems as CentOS or Ubuntu Linux.
IT skill set on demand
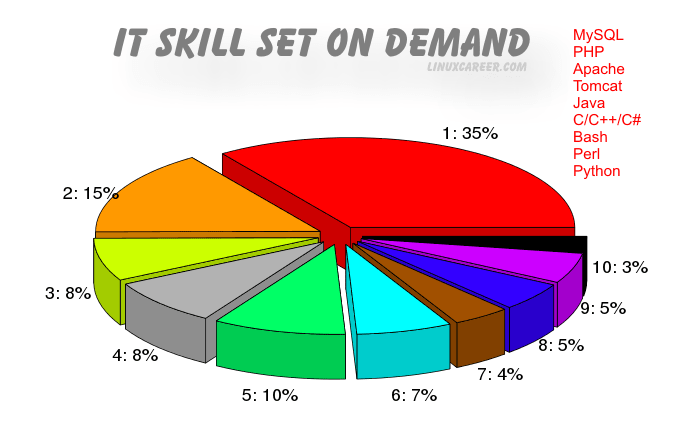
Since the identified ten clusters of skills contain various number of elements it would be incorrect to count the joined appearance of all skills from a group in a Linux job ad. This would give groups with less skills an advantage. Therefore, in order to identify the most popular group of IT skills in terms of demand, we have decided on tracking the frequency of appearance of two or more skills, from each of 10 groups, in Linux job ads.
The percentage of job ads satisfying our criterion for each of 10 identified groups of IT skills is reported in the pie chart[6] below. The first group of skills was categorized as the winner group of IT skills based on the highest demand. This group includes such skills as MySQL, PHP, Apache, Tomcat, Java, C/C++/C#, Bash, Perl and Python. The segment of skills in this group: MySQL, PHP, Apache, Tomcat is clearly related to LAMP administrators. It can be seen that the next most relevant skill to Linux, Apache, MySQL and PHP (LAMP in short) is Tomcat, which is understandable, since Tomcat is an Apache extension, which provides pure Java HTTP web server environment. Moreover, the second subgroup clusters programming languages such as: Java, C/C++/C#, Perl, Python and Bash scripting. This suggests that the most relevant additional skills to LAMP administrator are programming languages. Mastering the full set of those nine skills will equip you with qualifications for pursuing a Senior LAMP Administrator or Programmer/Developer career.
Conclusion
This report was based on the LinuxCareer’s IT Skills Watch and identified 10 clusters of IT Skills by studying their pairwise appearance in IT job advertisements. Additionally, the most popular in terms of demand set of IT skills was identified to be the group of Linux administrator/programmer skills.
References
[1] IT skills classification diagram created by GNU R. Relevant package: ape.
[2] http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cluster_analysis
[3] http://blogs.vmware.com/networkvirtualization/2013/06/vmware-red-hat-summit-more-customer-choice-for-openstack-2.html
[4] https://www.suse.com/partners/alliance-partners/sap/
[5] http://goo.gl/QNJWnc
[6] IT skills set on demand graph created by GNU R. Relevant package: plotrix.
Liability disclaimer
The information contained on this page is provided in good faith, and every reasonable effort is made to ensure that it is accurate and up to date. Accordingly, this information is provided 'as is' without warranty of any kind. LinuxCareer excludes all warranties, either express or implied (including, but not limited to any implied warranties of merchantability, fitness for a particular purpose, satisfactory quality or freedom from hidden defects). In no event shall LinuxCareer be liable for any damage arising, directly or indirectly, from the use of the information contained on this page including damages arising from inaccuracies, omissions or errors.
Any person relying on any of the information contained on this page or making any use of the information contained herein, shall do so at its own risk. LinuxCareer hereby disclaims any liability and shall not be held liable for any damages including, without limitation, direct, indirect or consequential damages including loss of revenue, loss of profit, loss of opportunity or other loss.

